M² - Beam Propagation Analysis
M² - Beam Propagation Analysis
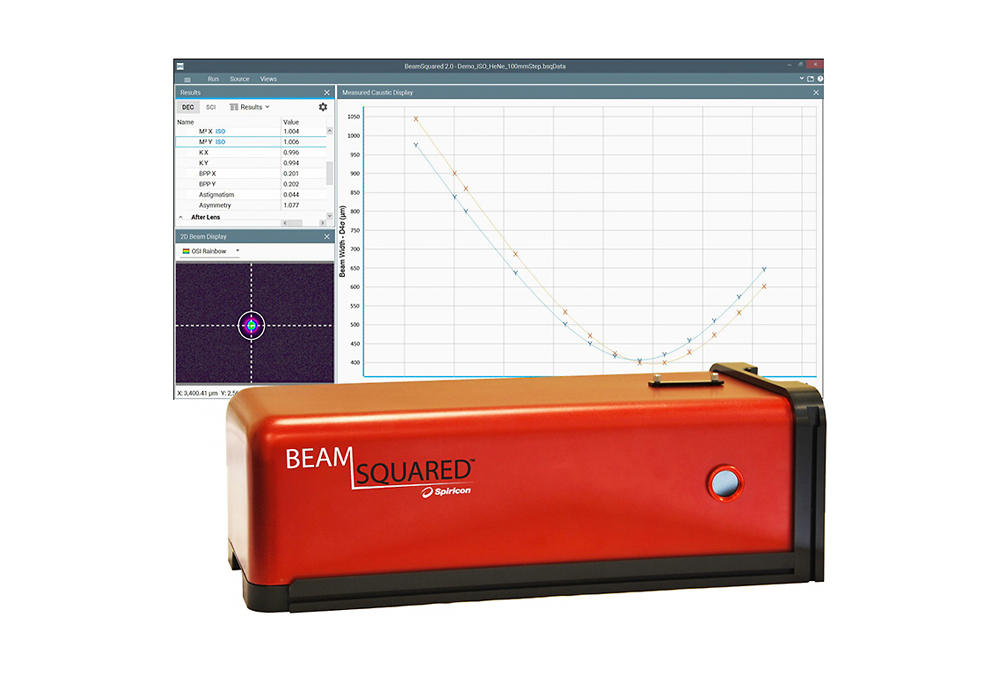
Product name : M² - Beam Propagation Analysis
Description :
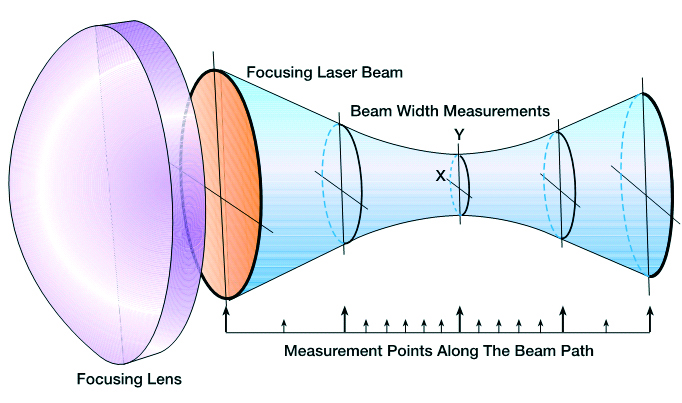
M², or Beam Propagation Ratio, is a value that indicates how close a laser is to being a single mode TEM00 beam, which in turn determines how small a beam waist can be focused. For the perfect Gaussian TEM00 condition the M² equals 1. M² cannot be determined from a single beam profile measurement. The ISO/DIS 11146 requires that M² be calculated from a series of measurements. M² is measured on real beams by focusing the beam with a fixed position lens of known focal length, and then measuring the characteristics of the artificially created beam waist and divergence. We have a number of solutions for the measurement of M² ranging from simple manual processes to fully automated dedicated instruments, depending on the frequency of the need to measure M² of lasers and laser systems.
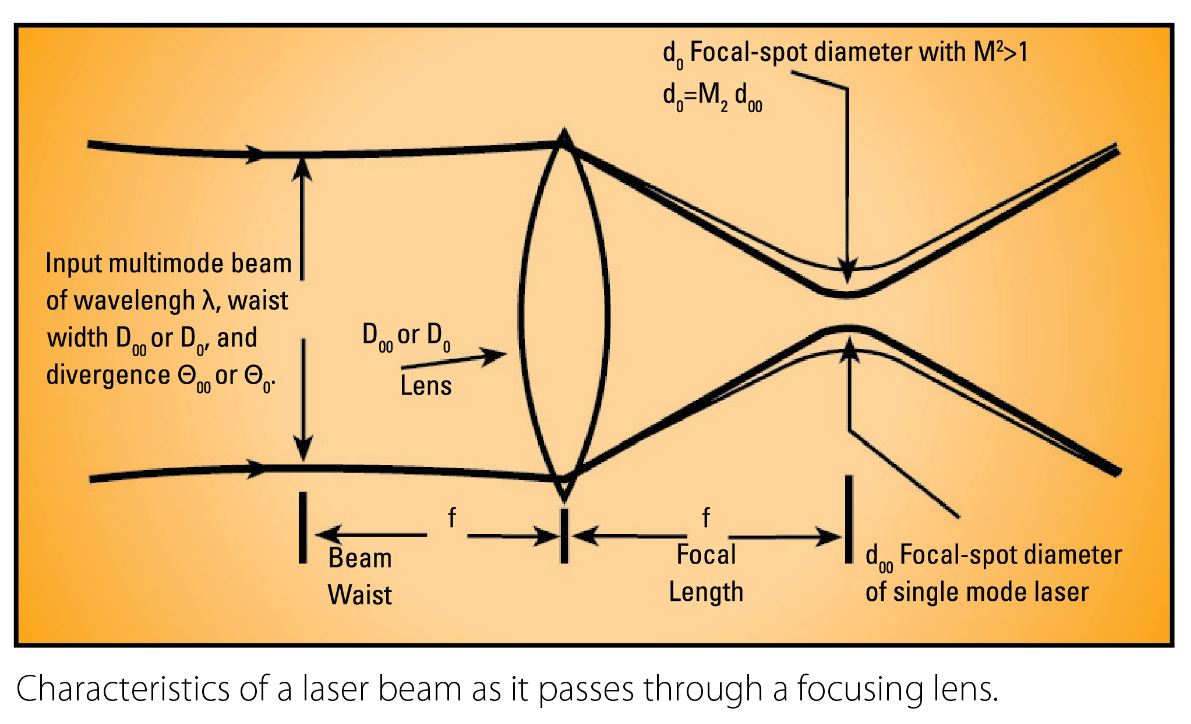
θ0 = M24λ/πD0
d0 = 4λ/πθ
| Model | Description | Price(USD) | Quantity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | BSQ-SP300 | BeamSquared Camera Based Beam Propagation Analyzer: M² | - |